
Data science has become a powerful tool across industries, unlocking new levels of efficiency, accuracy, and innovation. From predicting patient outcomes to optimizing retail inventory, data-driven decisions are shaping the future of business and society. In this blog post, we’ll explore practical use cases of data science in various sectors, including healthcare, finance, retail, and sports, showcasing its profound impact and relevance.
1. Healthcare: Data Science for Predictive Analytics and Personalized Medicine
In healthcare, data science is revolutionizing patient care, diagnosis, and treatment. By analyzing vast amounts of medical data, healthcare professionals can predict patient outcomes, detect diseases earlier, and offer more personalized treatments.
Key Use Cases:
- Predictive Analytics in Disease Prevention: Hospitals and research institutions use predictive models to analyze patient data, identifying individuals at high risk for chronic diseases like diabetes or heart disease. For example, by analyzing lifestyle data, genetic factors, and medical history, doctors can take preventive actions before a condition worsens.
- Personalized Medicine: Data science enables precision medicine, where treatment plans are customized to a patient’s genetic makeup and health data. AI-driven models can recommend the most effective drug or treatment based on a patient’s unique biological profile, increasing the chances of success.
- Medical Imaging Diagnostics: Data science is also being applied in radiology and medical imaging. Machine learning algorithms analyze X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to identify patterns, such as early signs of cancer, far more accurately than human interpretation. AI analyzing medical imaging data.
Impact: Data science is improving patient outcomes, reducing hospital readmissions, and making healthcare more proactive and personalized.
2. Finance: Risk Management and Fraud Detection
The finance sector is highly dependent on data science for various operations, including risk management, fraud detection, and investment strategies. With huge volumes of transactional data generated daily, financial institutions rely on data science techniques to maintain security and profitability.
Key Use Cases:
- Risk Management: Banks use predictive modelling to assess credit risk before approving loans. By analyzing historical customer data, such as spending behaviour and credit scores, data-driven models can predict the likelihood of default. This minimizes the risks associated with lending and investment decisions.
- Fraud Detection: Data science enables real-time fraud detection systems by analyzing transaction patterns and flagging suspicious activity. For example, credit card companies employ machine learning models that detect anomalies in spending behaviour, alerting users of potential fraud before any serious damage is done.
- Algorithmic Trading: In investment banking, data science powers algorithmic trading systems that make high-speed, data-driven trading decisions. These systems analyze market trends, historical data, and external factors like news or social media sentiment to optimize trading strategies.Example of fraud detection algorithms analyzing transactions.
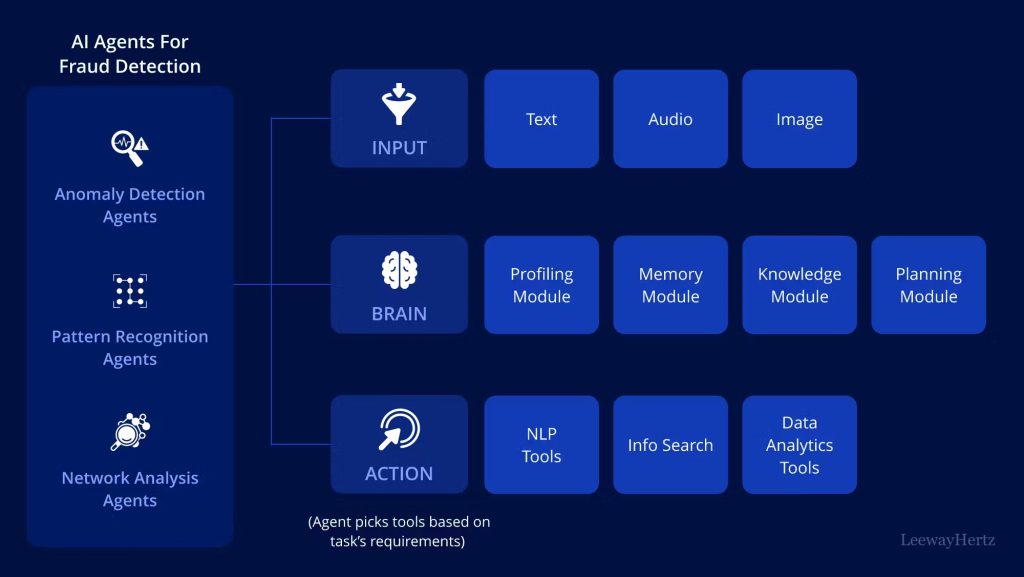
Impact: Data science is helping financial institutions mitigate risks, prevent fraud, and make more informed investment decisions in real-time.
3. Retail: Enhancing Customer Experience and Supply Chain Optimization
In the retail industry, data science is driving smarter business strategies, from personalizing customer experiences to optimizing supply chains. With a deeper understanding of customer behavior and market trends, retailers are improving their operations and sales outcomes.
Key Use Cases:
- Personalized Recommendations: Retailers like Amazon and Netflix leverage data science algorithms to analyze customer behaviour, purchase history, and preferences. This allows them to recommend relevant products or content, increasing user engagement and conversion rates.
- Demand Forecasting and Inventory Management: By analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and even weather patterns, retailers can accurately forecast demand for products. Data science models help retailers optimize inventory levels, ensuring products are available when customers want them without overstocking.
- Dynamic Pricing: Data science is used to implement dynamic pricing strategies, adjusting prices based on real-time factors such as demand, competitor pricing, or time of day. For example, e-commerce platforms can increase or decrease prices on popular products based on how quickly inventory is selling, maximizing profitability.
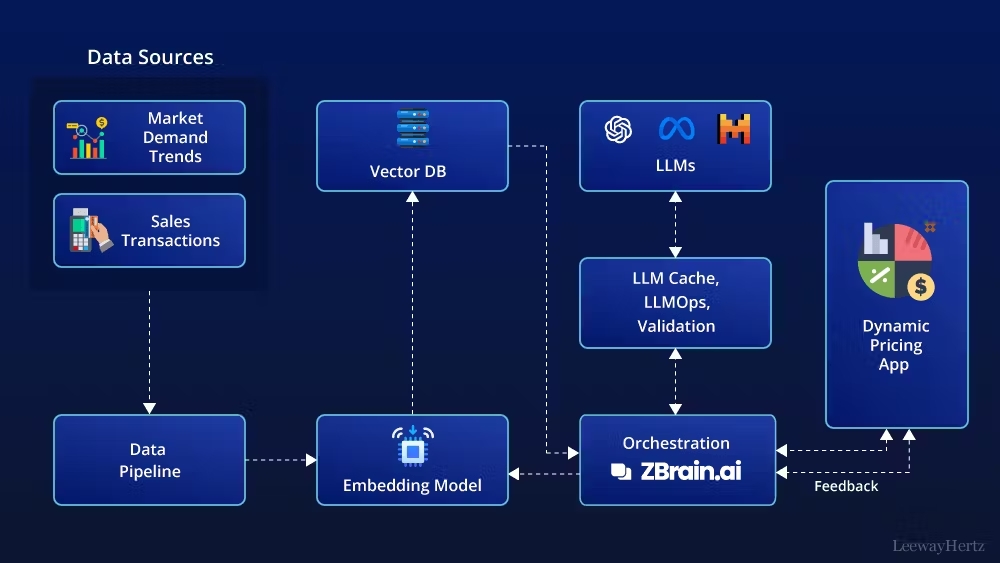
Impact: Data science is transforming retail by offering personalized customer experiences, optimizing supply chains, and driving revenue through better demand forecasting and pricing strategies.
4. Sports: Performance Analysis and Fan Engagement
Data science is becoming a key component in the sports industry, both on and off the field. From optimizing player performance to engaging fans through data-driven content, sports organizations are reaping the benefits of advanced analytics.
Key Use Cases:
- Player Performance and Injury Prevention: Teams use wearable sensors and data analysis to monitor players’ physical performance during training and games. By analyzing data on speed, heart rate, and movement, coaches can make better decisions about player fatigue, substitutions, and injury prevention.
- Game Strategy Optimization: In competitive sports, data analysis is used to optimize game strategies. For example, basketball teams use data to determine optimal shot locations, while soccer teams analyze positional data to improve passing strategies.
- Fan Engagement and Marketing: Sports organizations use data science to enhance fan experiences by analyzing social media trends, ticket sales, and in-game behaviors. This allows teams to tailor marketing campaigns, improve ticket pricing strategies, and offer personalized content to fans, increasing overall engagement.

Impact: Data science is enhancing athletic performance, reducing injury risk, and fostering stronger connections between teams and fans through targeted engagement strategies.
Conclusion
Data science is no longer just a buzzword—it’s a transformative force reshaping industries across the board. In healthcare, finance, retail, and sports, data-driven decisions are leading to improved outcomes, optimized operations, and enhanced user experiences. As industries continue to harness the power of data science, the possibilities for innovation and growth are endless. Whether it’s predicting health outcomes, stopping financial fraud, optimizing retail sales, or improving player performance, the practical applications of data science are making a profound impact on our world. And this is only the beginning.











